One feature I’ve not appreciated enough in the past in SQL Server is Resource Governor.
Resource Governor allows you to fix problems with Memory Grants in a simple way, as Erik Darling recommends. It also lets you classify sessions into groups and limit the maximum number of simultaneous requests, and /or limit the degree of parallelism if you need more CPU for other workloads. While this will slow down the queries you classify into that group, this can be super useful, especially if you’re already using something like Snapshot isolation to prevent blocking or you are using a read-only replica.
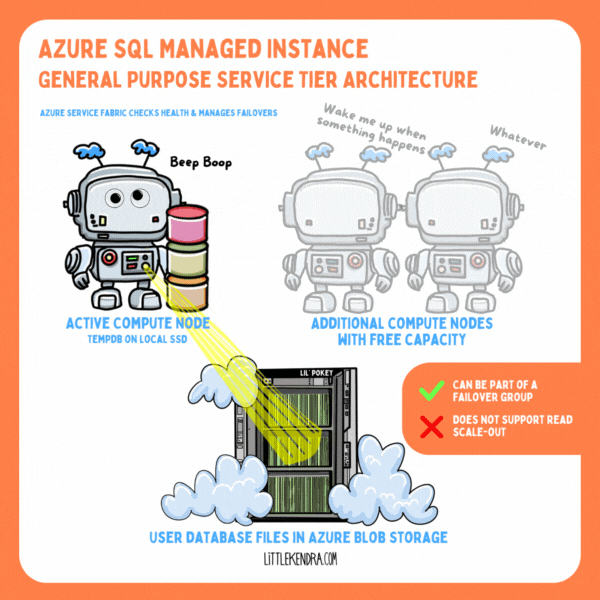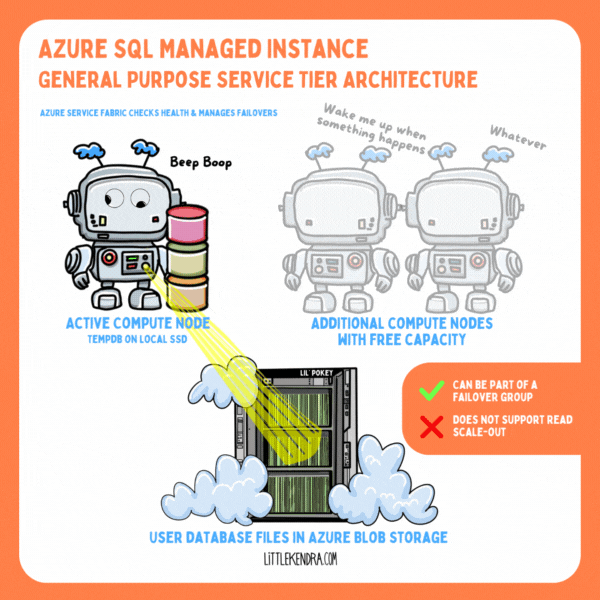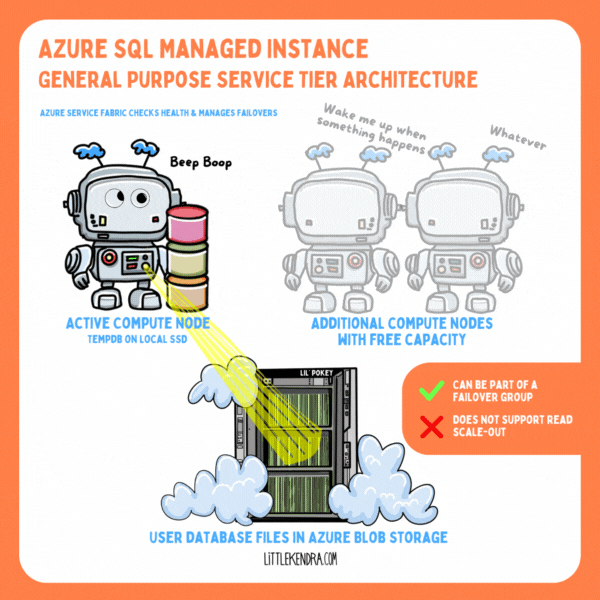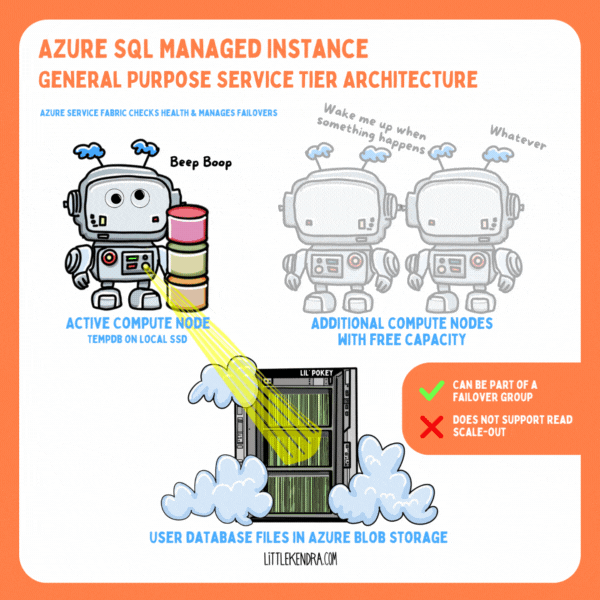
In Azure SQL Managed Instance, you get to use Resource Governor, even in the General Purpose tier. This is awesome.
Just make sure you execute commands in the context of the master database, or you’ll get error 40510: Statement 'ALTER RESOURCE GOVERNOR' is not supported in this version of SQL Server.
It is supported! Just USE master; before running your commands.
Continue reading